
CHEVAL Boris
- Psychology, École normale supérieure de Rennes, Bruz, France
- Exercise & Sports Psychology, Health & Disease, Physical Activity
- recommender
Recommendations: 2
Reviews: 0
Recommendations: 2
Development and validation of the Value of Physical Effort (VoPE) scale
Capturing Individual Differences in the Valuation of Physical Effort
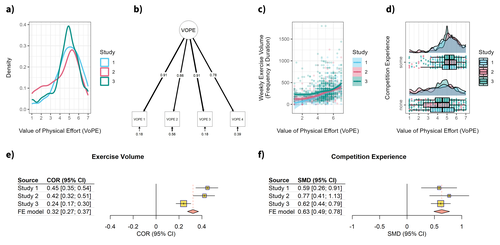
Recommended by Boris Cheval based on reviews by Silvio Maltagliati and Erik BijleveldHowever, beyond this general view of physical effort as an aversive experience to be avoided, substantial individual differences in the valuation of physical effort have been observed. This suggests that some individuals may actually evaluate physical effort positively. Contrary to the law of least effort, these individuals may prefer behavioral alternatives that require more effort, all else being equal (Inzlicht et al., 2018). Until the development of the Physical Effort Scale (Cheval et al., 2024) and the present work by Bieleke et al. (2024), no formal scale existed to capture such individual differences in the valuation of physical effort. The primary goal of the present study was to design, develop, and validate such a scale.
To achieve this goal, the authors conducted three independent studies (total N = 1,364) to establish the psychometric properties of the Value of Physical Effort (VoPE) scale (Bieleke et al., 2024). Across these studies, using both cross-sectional and longitudinal designs and a variety of statistical techniques (e.g., psychometric network analysis, elastic net regression), results indicated that the VoPE scale has robust associations with physical activity behaviors, strong test-retest reliability, and captures unique variance in predicting exercise behaviors. Taken together, these findings suggest that the VoPE scale is a valid and reliable measure of individual differences in the valuation of physical effort.
Bieleke M, Stähler J, Wolff W, Schüler J. Development and validation of the Value of Physical Effort (VoPE) scale.PsyArXiv. 2023, version 5. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/pqw26. Peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Health and Movement Sciences. https://doi.org/10.24072/pci.healthmovsci.100115
Cheval B, Boisgontier MP. The theory of effort minimization in physical activity. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2021;49(3):168-178. https://doi.org/10.1249/JES.0000000000000252
Cheval B, Maltagliati S, Courvoisier DS, Marcora S, Boisgontier MP.Development and validation of the physical effort scale (PES). Psychology of Sport and Exercise. 2024;72:102607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychsport.2024.102607
Inzlicht M, Shenhav A, Olivola CY. The effort paradox: effort is both costly and valued. Trends Cogn Sci. 2018;22(4):337-349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2018.01.007
On the specifics of valuing effort: a developmental and a formalized perspective on preferences for mental and physical effort
Is effort evaluation domain-specific or general?
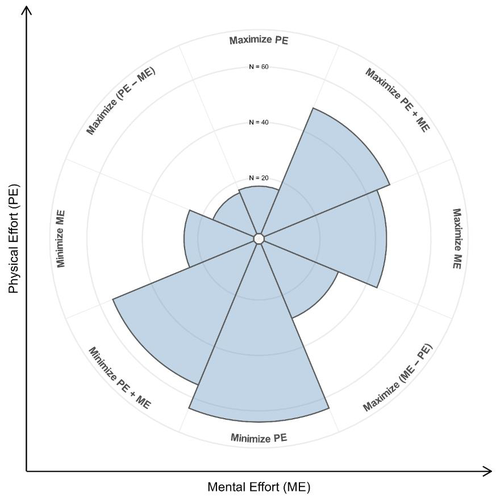
Recommended by Boris Cheval based on reviews by James Steele, Ines Pfeffer and 1 anonymous reviewerThe law of least effort suggests that, certis paribus, people tend to exert as little effort as possible when engaged in a goal-directed task (Cheval & Boisgontier, 2021). At the same time, however, large interindividual differences in the processing of effort have been observed, suggesting that effort per se can sometimes be valued positively (Inzlicht et al., 2018). However, until the present study by Wolff et al. (2024), all previous studies had largely ignored whether these individual differences in the valuation of effort might depend on the context (mental versus physical), i.e., in layman's terms, we do not know whether people value any effort or whether these preferences are specific to the mental and/or physical domain. The aim of the present study (Wolff et al., 2024) was to answer this question on the basis of two independent studies.
Study 1 (N = 39) used a binary decision task to measure preferences for allocating mental versus physical effort and showed that people differ markedly in their preferred allocation of effort. Crucially, a disposition to value mental effort (as assessed by the Need for Cognition Scale) was associated with a higher preference for mental effort, whereas a disposition to value physical effort (as assessed by the recently developed Value of Physical Effort Scale) was associated with a preference for physical effort.
Study 2 (N = 300 students) confirmed the robustness of the findings and showed that the tendency to value mental effort was associated with better grades in math (but showed no evidence of such an association in sport), whereas the tendency to value physical effort was associated with better grades in sport (but showed no evidence of such an association in math). Furthermore, the study extended these findings by showing that valuing physical effort was associated with less boredom in sports, whereas valuing mental effort was associated with less boredom in math.
In summary, the results of this research provide the first evidence suggesting that the valuation of effort is domain-specific rather than general. This finding paves the way for future research aimed at improving our understanding of the valuation of physical or mental effort. This article makes an important contribution to the knowledge of the key issues surrounding whether effort valuation is domain-specific or general.
Since all reviewers have indicated that they are satisfied with the authors' revision, which accurately and comprehensively addresses the reviewers' and my comments, it is my pleasure to recommend this preprint.
Cheval B, Boisgontier MP. The theory of effort minimization in physical activity. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2021;49(3):168-178. https://doi.org/10.1249/JES.0000000000000252
https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/ycvxw